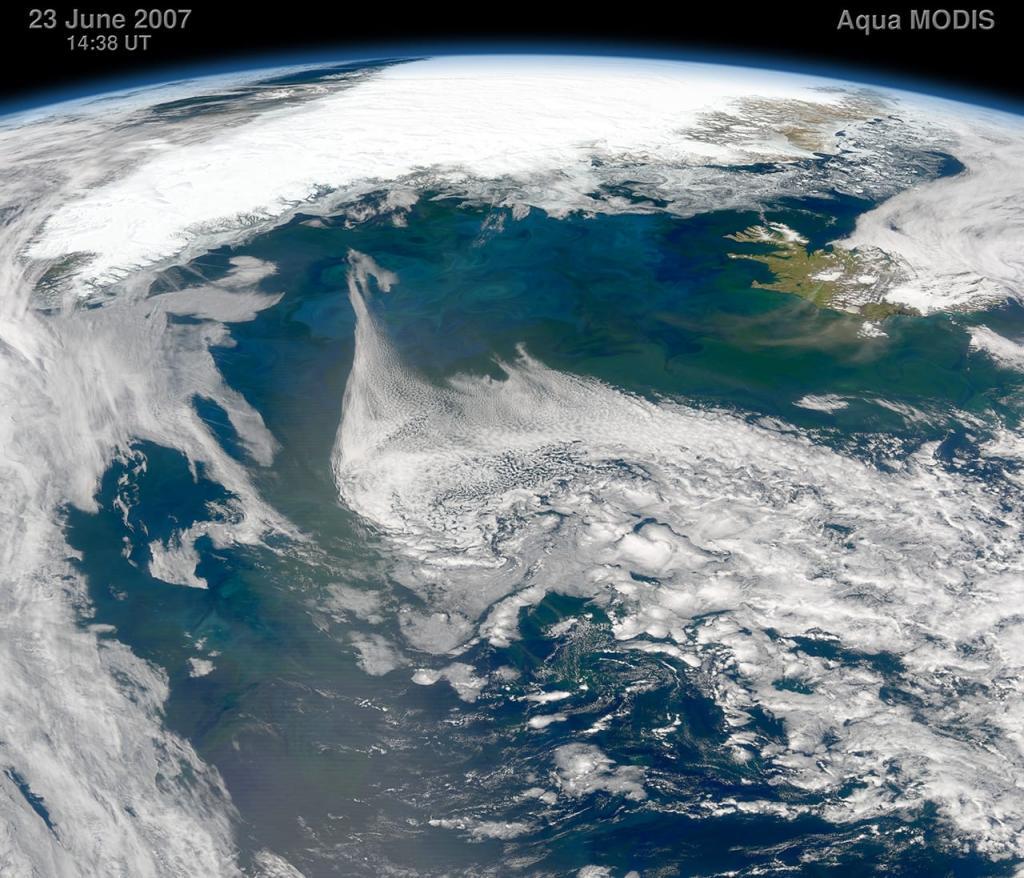
© Algal blooms in the North Atlantic - a mosaic of green swirls reaches the productive and dynamic waters of the subarctic Atlantic Ocean, (c) NASA

© Matthew Osman (left) and Mike Waszkiewicz position an ice core during a storm in West Greenland. (c) Sarah Das, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution

© An Air Greenland helicopter takes off with a load of ice cores, (c) Sarah Das, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution

© Drilling location team in Greenland (from left to right): Mike Waszkiewicz (US Ice Drilling Program), dr. Sarah Das, Matt Osman, dr. Luke Trusel (all WHOI), (c) Sarah Das, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
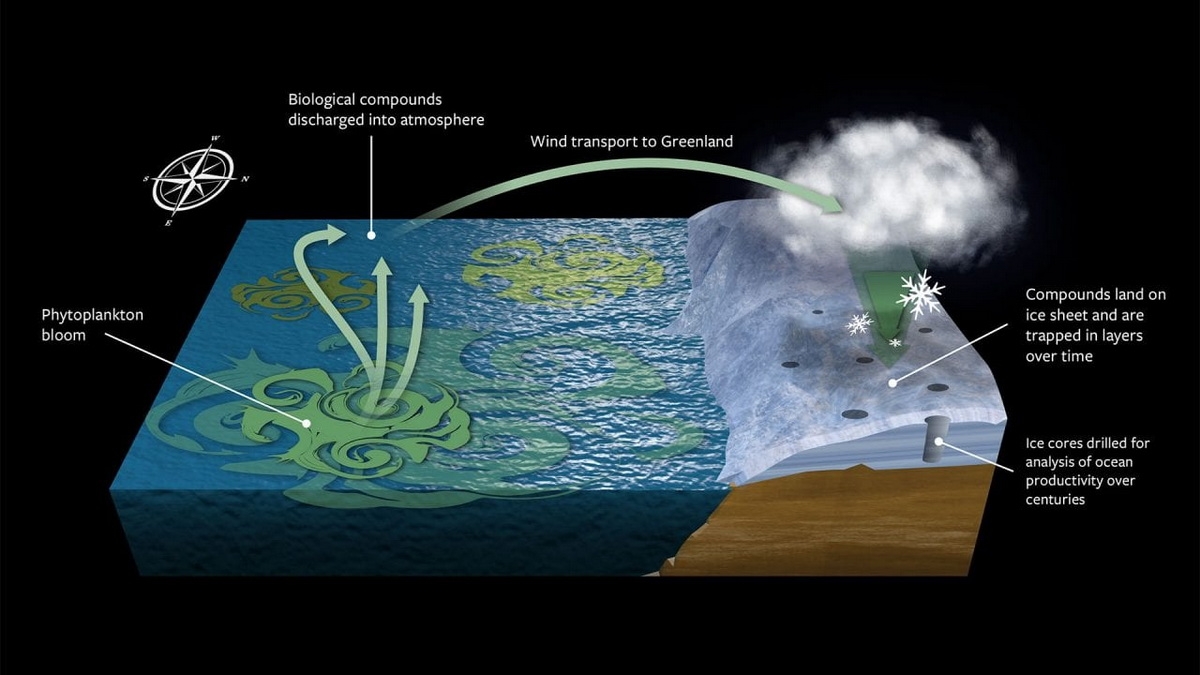
© The diagram illustrates how biological compounds from phytoplankton blooms enter the atmosphere and eventually end up in centuries-old ice cores. (c) Eric S. Taylor and Timothy Silva, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
The productivity of the North Atlantic has fallen by 10 percent in the industrial age
May 14, 2019
Less photosynthesis due to rising water temperatures
Practically all marine life depends on the productivity of phytoplankton - microscopic organisms that work tirelessly on the sea surface to absorb the carbon dioxide that enters the ocean from the atmosphere.
By means of photosynthesis, the algae split carbon dioxide into oxygen and organic carbon, which they store. This carbon is the basis of marine food webs, from the smallest shrimp to sea turtles to large humpback whales.
Now scientists from MIT, the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and other institutes have found evidence that the productivity of phytoplankton in the North Atlantic, one of the world's most productive marine areas, is steadily declining.
In a recent study published in the journal Nature, the researchers report that phytoplankton productivity in this important region has fallen by around ten percent since the beginning of the industrial era in the mid-19th century. This decline coincides with steadily rising surface temperatures over the same period.
Matthew Osman of the WHOI, lead author of the study, estimates that productivity of phytoplankton could continue to fall as temperatures rise as a result of man-made climate change.
"We should be worried," says Osman. "If we have a growing population but a diminishing food base, we will probably eventually feel the effects of this decline."
Osman and his colleagues looked for trends in the productivity of phytoplankton using the molecular compound methanesulfonic acid, MsOH for short. When phytoplankton expands into large flowers, certain microbes emit dimethyl sulfide or DMS, an aerosol that is released into the atmosphere and eventually disintegrates as either a sulfate aerosol or MsOH, which is then deposited by sea or land winds.
In the North Atlantic, the phytoplankton MsOH produced, which was deposited in the north, also in Greenland. The researchers measured MsOH in Greenland ice cores, representing layers of past snowfall events that have survived for hundreds of years.
The team analyzed a total of twelve ice cores, which were obtained from the 1980s to today at various locations on the Greenland ice sheet.
In all 12 ice cores, researchers observed a significant decline in MsOH concentrations since the mid-19th century, when large-scale greenhouse gas production began. This decline is directly linked to a decline in phytoplankton production in the North Atlantic.
"We are seeing a long-term decline in ocean productivity that occurs around the same time as the greenhouse gas emissions on an industrial scale began when the climate system began to malfunction," says Osman. "The North Atlantic is a very productive area, and there is a huge multinational fishing industry associated with this productivity, and any change at the base of this food chain will have cascading effects that we will eventually experience on our dining tables."